India is known as the pharmacy of the world, mainly because it supplies low cost generic medicine to most countries. Indian companies have profited immensely by releasing generic versions of innovative drugs at a fraction of the cost. Let’s take a look at what generic medicines are and why they can be sold for such low prices.
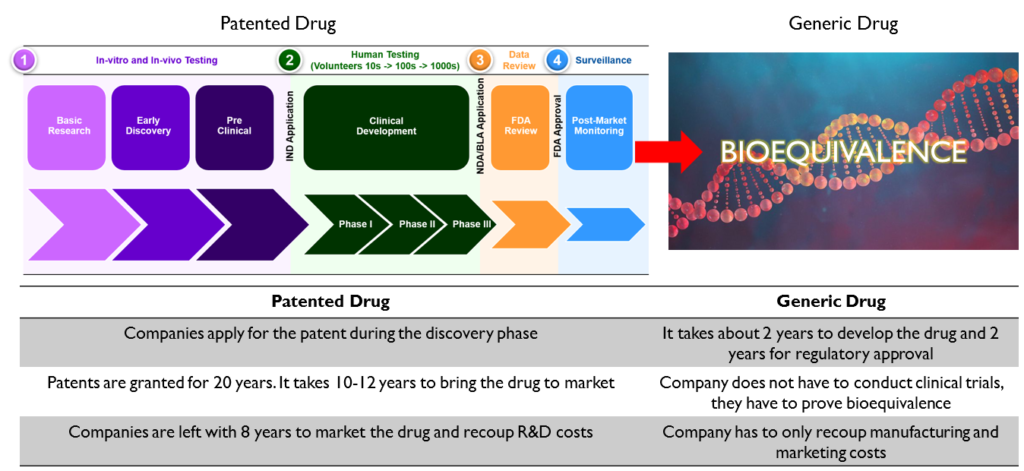
In our article about the drug discovery process, we explained the journey an innovative drug has to go through to make it to market. The innovative drugs are usually under patent which means that only the innovator is allowed to manufacture and market the drug. When the patent on a drug expires, generic drug manufacturers are allowed to sell copies of the innovator drug. They reverse engineer the product and are able to make a drug that is therapeutically equivalent to the original innovator drug. This type of drug is known as a generic drug.
Generic Drugs
A generic drug contains the same active ingredient as the original drug and has the same therapeutic effect. It should also have the same strength, safety, quality and dosage form. They have the same risks and provide the same benefits as the original innovator drugs. Generic drugs are usually much cheaper than the original drugs which is instrumental in bringing down healthcare costs.
What can be different?
Therapy wise, a generic has to be the exact same as the original drug. But generic drugs can be different from the original in some aspects. For starters, the name of the drug has to be different. Due to various trademark laws, generic drugs cannot have the same brand name as the original drug. Generic drugs are also allowed to use different excipients (inactive ingredients). They can use different bulking agents, stabilizers, different flavors and different colors. As a result, the taste and appearance of the drug can be different than the original drug. The generic can have a different shape in case of tablets as well. The price of the generic can and almost always is different from the price of the original drug.
Patent Cliff
When an innovator’s drug goes off patent, generic companies enter the market with copies which are sold for much cheaper than the original. This causes a sharp decline in sales for the innovator in the year following the patent expiry. This phenomenon is called the patent cliff. The patent cliff’s effects are more severe for blockbuster products (products with annual sales of over $1 Billion). The increase in competition post patent expiry causes a reduction in the price of the drug. This decline is most evident in oral medicines like tablets or capsules. But overall, the price of all medicines decline by 10-15% each year until they stabilize at 19-20% of the cost of the original patented drugs.
Why are they so much cheaper?
Innovators file a patent for the new drugs they bring to market. They invest hundreds of millions and in a lot of cases billions of dollars into the discovery and trials of these drugs. Drug patents are given for about 20 years and are usually filed at the time of discovery which is about 10-12 years before the drug receives approval for sale to the general public. The drug development process takes about 10-12 years, which means that the innovator has about 8-10 years of exclusivity during which he has absolute pricing power. The innovator usually prices the drug at a huge premium to recoup his investment in the development of the drug as well as the cost of failed drug candidates.
A generic drug manufacturer does not have to go through the costly drug development process. Their R&D costs are limited to reverse engineering of the drug. They have to prove that their drug is bioequivalent to the original drug. Bioequivalent means that it contains the same active ingredient and has the same effect on the body as the original drug. Since the cost to develop a generic is very low compared to the original, companies can sell the generic version of drugs for a fraction of the original.
Types of Generics
There are four main types of generic drugs – Unbranded or Commodity Generics, Branded Generics, Authorized Generics and Specialty Generics.
Unbranded generics, also known as commodity generics are drugs that are sold just by the name of the API in the drug. They are not differentiated products and do not have any branding or need any sort of marketing. These are mostly bought by institutions and governments who provide medication to the masses and don’t want to pay a premium for the brand name drug. For example, a government buying a large quantity of drug to distribute for free will buy a commodity generic version going by the name of the drug itself – like paracetamol.
Branded generics are the exact same drug sold by pharma companies but with branding. For example, the most popular branded generics for paracetamol in India are Crocin or Dolo. They are the exact same drug, but the company can charge a premium for their brand as they also incur branding and marketing costs. These drugs are mostly sold to the public rather than institutions as the public actually prefers brands and are willing to pay a small premium for the assurance of quality.
Authorized generics are the exact same drug sold by the company that held the patent for it. A company will not discontinue the product just because the patent has expired. Instead, they will lower the price of their drug and sell it as an authorized generic often for a slight premium over branded generics. Authorized generics are exactly the same as the original drugs with the exact same excipients, shape and size.
Specialty generics are generic versions of specialty drugs. Specialty drugs are high value drugs that are used to treat chronic and complex diseases. These are very expensive drugs and their generic versions will also sell at a higher cost than simple generics.
Approval Process
While innovative drugs have to file a New Drug Application (NDA) post the successful completion of clinical trials, generic companies have to file an ANDA – Abbreviated New Drug Application. It is called abbreviated because generic drug manufacturers do not have to perform clinical trials for their drugs and hence the approval process is much shorter. An ANDA usually contains bioavailability and bioequivalence studies. Once it has been approved, the generic drug manufacturer can market and sell the drugs in the United States.
In the ANDA application, the generic company must submit to the FDA a certification regarding the patent of the original drug. These are called paragraphs.
- Para 1 certification states that there are no listed patents for the generic drug. In this case, the FDA may approve the drug immediately. These drugs usually face a lot of competition and are basically commodities.
- Para 2 certification states that the listed patent for the drug has expired. In this case too, the FDA may approve the drug immediately and the competition in these drugs is high as well.
- Para 3 certification states that the patent on the listed drug has not expired and will expire on a particular date. In this case, the FDA may approve the drug with effect from the date of patent expiry.
- Para 4 certification is the most important out of these. In a Para 4 filing, a generic company will challenge the patent of the innovator stating that the patent is invalid and should not have been granted in the first place or that the generic does not infringe on the patent. The first generic company to challenge the patent in court and win is granted 180 days of exclusivity to market the drug. This means that no competition can enter the market for 6 months. This is an incentive given by the FDA to the generic companies to take down fraudulent patents and thus greatly reduce the price of the drug. This is a very profitable strategy that almost all Indian generic drug companies have used in the past. In 2012, Indian pharma companies were involved in at least 50% of the Para 4 litigations in the US.
Why are generics important?
Generics play a very important role in bringing down the cost of healthcare. In poor and developing countries, where people cannot afford the high costs of patented drugs, generic medicines have saved and improved a lot of lives. Healthcare costs in the developed countries have increased at a very fast pace and wages have not kept up. Innovative drugs are very important to the advancement of healthcare and being able to treat or cure diseases that we could not previously. But when these drugs are first introduced to the market, they are out of the reach of people who do not have health insurance.
Generic drugs are important to bring down the price of these drugs so that the masses have access to it. The penetration of generics has been increasing over the years and is the highest in the United States where healthcare costs have spiralled out of control. Generic drugs make up 90% of the volume of drugs sold in the US but only 22% of the value. The timely approval of generic drugs is essential to make healthcare available for all.